Chercher
 Coltura Promiscua inFrance
Coltura Promiscua inFranceResearch & upload: Bénédicte Gaillard: The entries are still in process, the e-atlas is still under development.
This technique is known since the Antiquity.
[Read more]The entries are still in process, the e-atlas is still under development
Dehesas always existed but are now tremendously diminishing and are being replaced. This evolution is mainly due to the increase of intensive agriculture, to the development of enclosed fields and to the high level or urbanisation.
[Read more]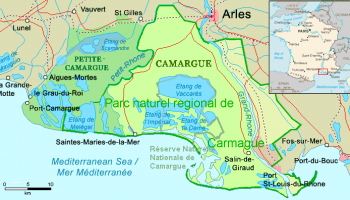 Paysages de delta inFrance
Paysages de delta inFranceThe entries are still in process, the e-atlas is still under development
The Delta du Rhône was formed 10.000 years ago by the penetration and decline of the sea and the edification of sandy spits.
[Read more] Enclosed land inFrance
Enclosed land inFranceResearch: Alexandra Kruse & Bénédicte Gaillard; upload: Bénédicte Gaillard. The entries are still in progress.
[Read more]
The entries are still in process, the e-atlas is still under development
It started around the year 1000 after JC.
[Read more]Research & upload: Bénédicte Gaillard. The entries are still in process.
The Neolithic Revolution leading from nomadic to sedentary lifestyle has engendered an evolution from hunter-gatherer to sheep and cattle breeding, the cultivation of wheat and barley grains, on the territory of France around the 5th Century before JC. From this period on man works and plough the soil.
[Read more] Hay making structures inFrance
Hay making structures inFranceResearch: Alexandra Kruse & Bénédicte Gaillar; upload: Bénédicte Gaillard. The entries are still in process.
[Read more]
Some writings about orchards in France dating from the 16th Century have been found.
[Read more]Research: Alexandra Kruse & Bénédicte Gaillard; Upload: Bénédicte Gaillard. The entries are still in process
Artificial terraced landscape date back early and historical findings prove wine cultivation at the rivers through Romans. They already used prepared terraces for the cultivation.
[Read more] Water grasslands inFrance
Water grasslands inFranceResearch: Bénédicte Gaillard & Alexandra Kruse; upload: Bénédicte Gaillard: The entries are still in process
[Read more]
 Prairies boisées inFrance
Prairies boisées inFranceResearch: Yves Michelin et al, Alexandra Kruse, Bénédicte Gaillard; upload: Bénédicte Gaillard: The entries are still under process.
[Read more]
Farmland in France
It is dominant and characteristic of the landscape since it represents half of the national territory, it represents 3,5% of the gross domestic product of the country, there are 348.000 agricultural exploitations and 770.000 people fully employed in this sector.
The surface of agricultural land is divided as such:
18,4 millions of ha of arable soils among them cereals (9,4), temporary grassland and annual crop (4,9), oleaginous (2,3), other annual cultivation (1,3) and fallow land (0,5)
1 million of ha of permanent cultivation (orchards, vineyards)
7,7 millions of ha of permanent grassland
1,9 million of ha of agricultural land used off-farm among them collective grassland and off-field (1,8) and family gardens and orchards (0,1)
This surface is constantly decreasing because of the augmentation of wooded surfaces and mainly artificialised (modified) surfaces (around 3,4 millions of ha of built surfaces, covered or rendered unfit to cultivation:
*Not built (0,8 million of ha) corresponds to surfaces such as construction sites, quarries, court yards, pleasure gardens, waste lands, cemeteries)
*Covered soils (1,7 million of ha) correspond to roads and park places
*Built soils (0,9%) receive new constructions
Coltura Promiscua in France
It still occurs in the vineyards of Alsace, but it is rare: 74ha or 0,5% of the vine production in Alsace.
In Normandie the complantation with apple or pear trees can been found in semi bocage enclosed fields. In Alsace they are found on the vineyards and in Provence they took place on the Lure mountain.
Wooded grasslands in France
For this entry, the example of the Var region in the South East of France has been taken.
The agro-sylvo-pastoralism in the Var region is a system of mixed production: extensive animal production, intensive fodder corn production, orchards etc. (chestnut, olives, wine,…).








